Mechanism of restructuring the company as part of its innovation strategy
Annotation. The need for research of restructuring mechanism of companies under the conditions of innovation and investment development becomes the most strategically important. The research has improved: scientific and methodological approaches to the formation of the mechanism of the enterprise restructuring, which in comparison with the current ones, reflects the modern terms of innovation and investment development of the country’s economy as well as a set of key elements of restructuring implementation, which include: types, strategies, methods, tools, and levers. The further development has been implied to structuralization of organizational and financial methods of companies restructuring, among which the method of corporate structuring has been distinguished. The research focuses on this particular method. Among restructuring strategies the strategies for introducing innovations (modernization of production, introduction of innovative technologies, development of new types of products and services) and strategies for diversification, mainly production of goods (operations, services), have been identified. It has also been revealed that the top 5 companies with the highest innovation indexes described in this paper belong to such industries as logistics, engineering, pharmaceuticals, fuel and energy
Keywords: restructuring,company, integration, corporatization, innovation index.
Introduction. Topicality of the research. Need in efficiency increase of restructuring measures at the national business entities, in particular in the context of innovation and investment development of Ukrainian companies, necessitates studying the application of the newest restructuring forms of company management in terms of post-crisis operation of Ukrainian economic system, like in everywhere in the world (Zeman et al, 2018, Zeman & Lentner, 2018).
Literature review. There is a wide range of scientific publications on this subject, in particular the works of such scholars as: S.O. Arefiev (Arefiev, 2014), S. Commander (Commander, 1998), V.G. Prushkivskyi (Prushkivskyi, 2008), O.Y. Savruk (Savruk, 2010), K. Santarek (Santarek,2011 ) and others. The scholars who study the following topic are as follows:
A. Amsden, J. Kochannowicz and L. Taylor (Amsdenet al, 1994),
I. Goldberg and A. Watkins (Goldberg and Watkins, 2000),
V. Carlin, C. Mayer, H.-W. Sinn and V. Grilli (Carlin et al, 1992), N.Stojčić (Stojčić, 2012) and others. The following scholars and their publications are to be mentioned: S. Djankov and
P. Murrell (Djankov and Murrell, 2002), O.V. Kostiunik and A.A. Nakonechna (Kostiunik and Nakonechna, 2016),
F. Montes-Negret and L. Papi (Montes-Negret and Papi, 1997), J. Charap and A. Zemplinerova (Charap and Zemplinerova, 1993) and others.
Research objective. The research aims at systematizing the existing approaches to the restructuring essence, development of it several objective and asset of goals as well as to the development of methods, tools, mechanisms of restructuring of national companies under the conditions of innovation and investment development of the economy; proving the effectiveness of using the method of corporate structuring as a restructuring form in the management system of national companies (in particular, in the context of innovation and investment development); substantiating the author’s vision of the directions of improving the companies’ efficiency on the basis of restructuring measures in modern economic conditions. Scientific novelty of the research. The research has improved:
- scientific and methodological approaches to the formation of the mechanism of the enterprise restructuring, which in comparison with the current ones, reflects the modern terms of innovation and investment development of the country’s economy as well as a set of key elements of restructuring implementation, which include: types, strategies, methods, tools, and levers.
The further development has been implied to:
- structuralization of organizational and financial methods of companies restructuring, among which the method of corporate structuring has been distinguished. The research focuses on this particular method. Among restructuring strategies the strategies for introducing innovations (modernization of production, introduction of innovative technologies, development of new types of products and services) and strategies for diversification, mainly production of goods (operations, services), have been identified.
1. Mechanism of restructuring the company. Based on the definition of the term “restructuring” provided in this research (as stated above), its key element is a particular mechanism (see Figure 1). In this context, one of the main elements of such a mechanism is strategic and operative restructuring. It is necessary to state that the global development of the world economy, including in Ukraine, should be oriented towards the strategic restructuring of national enterprises and companies. Operational restructuring can be part of a general strategy for the development of companies and their associations, because it should be oriented to the needs and commercial interests of the relevant corporate structure of these companies.
Making the decision on the usage of strategic and operative restructuring, top managers and owners of economic entities must understand their advantages and disadvantages. Thus, advantages of strategic restructuring include the following items: influence on all spheres of the company operation without any exceptions; formation of new, more effective organizational, management and production structure of business entities; receive of long-term competitive advantages; synergetic effect from the realization. At the same time, strategic restructuring has some disadvantages, in particular: terms of realization; complexity; the cost of implementation; considerable specific demands to the personnel, mainly to the top managers – it often demands attraction of outside executors. The benefits of operative restructuring are as follows: the speed of implementation; a relative simplicity; a target direction of the influence by developed restructuring measures; a relatively low cost. The negative sides of operative restructuring are: possibility to get negative consequences due to incoherence of employees’ actions; relatively weak influence of restructuring measures on the company as the whole; the complexity in priorities determination while restructuring implementation because of a considerable rate of deficit in financial resources.
The method of corporate structuring should be allocated among organizational methods of restructuring. Below in this research the main emphasis will be mostly made on it. Thus, in the researches on the method of corporate structuring implementation as one of the forms of restructuring measures in the management system of business processes of integrated companies and companies, Yu.Mordvytska proves the high level of competitiveness and opportunities of national corporations and their subdivisions owned huge resources that can be directed to innovation and investment development of national economy as well (Mordvytska, 2016, p. 61; Mordvytska, 2016, p. 92). The maximum high potential of such a method of restructuring for the companies during all stages of their life cycle has also been identified.
One cannot ignore the effectiveness of financial methods in the context of restructuring, for example, such as optimization of pricing and taxation. Yu.Mordvytskain her studies on the effectiveness of transfer pricing in companies (Mordvytska, 2016, p. 63) clearly shows the relevant arguments and calculates the economic effect of the implementation of such restructuring measures.
In the context of the restructuring mechanism characterization of the company in modern terms of innovation and investment development of the country’s economy, the appropriate restructuring strategies need special attention. The strategies of innovation implementation are the most important and adapted for the economic entities on all stages of their life cycle. The key ones are: – modernization of production; – innovative technology implementation; – development of new types of goods and services. The group of strategies provided in the study allows in-depth restructuring at the company by choosing one of the ways that needs more changes in the context of reaching the overall objective and the set of goals during the certain stage of its life cycle (see above).
Fig. 1. Mechanism of the company restructuring in modern terms of innovation and investment development of the country’s economy
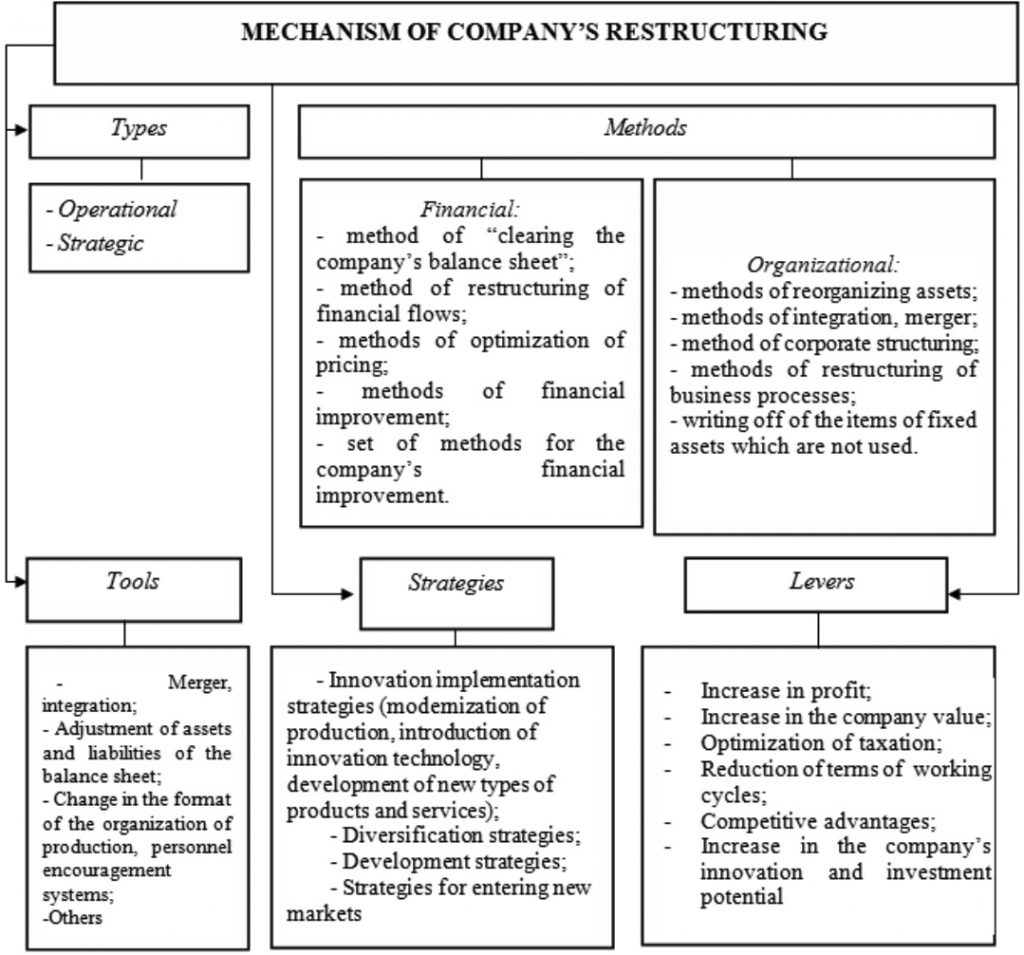
Source: improved by the author
Giving characteristics to the restructuring mechanism of the company in the modern terms of innovation and investment development of the country’s economy, tools that economic entities can use for their restructuring are to be studied (see Figure 1). The number and formation of the appropriate set of such tools within business entities restructuring depend on several factors, namely: – a phase of the company life cycle; – usage of the appropriate type (sub-type), strategy ( a set of strategies), methods (a set of methods) of restructuring; – specific nature of business unit realization of its financial and operational activities; influence peculiarities of external and internal environment factors; the quality of operation of state and municipal power bodies within innovation and investment development of the country’s economy. In the context of emphasizing the priority of corporate structuring methods within the company restructuring, the main attention is paid to such tools as takeover and integration.
Discussing levers that can be used within the company restructuring (see Figure. 1) and taking into account the separation of structuring methods as the priority ones for the economic entities in the modern terms of the national Ukrainian economic system transformation, the emphasis has been done on formation and maintenance of competitive advantages as well as the increase of innovation and investment potential of the company. The competitive advantages themselves plus development and implementation of innovation based on optimization of their investment support provide the company with the opportunity to realize effective restructuring regardless of both the life cycle stage which it undergoes and the influence of external and internal factors.
In general, the positive effects of restructuring are aimed at improving key operating and financial performance of companies; financial improvement; improvement of the level of attractiveness for investors, expanding its external financing, opportunity to develop and implement innovative technologies, solutions, know-how in operational activities, etc.
The current research outlines that forecasting and optimization of the growth rates of capital investments directed to restructuring and volumes of financing of innovations in the economy should be carried out by finding the ideal method of increasing the volume of capital investments into restructuring that leads to an increase in innovative investments of companies.
In this case for the tendencies connected with both capital investment into companies restructuring and innovative expenditure of economic entities, it is suggested to determine the significance of the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient for the two trends singled out in this research. It is necessary to calculate the critical point 1 to check the zero hypothesis about equality of the general coefficient of rank correlation at the level of significance α to zero.
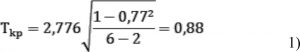
The correlation coefficient shows a significant correlation of 0,88, that is, it can be argued that there is a close correlation between investments and innovations. It should be noted that in order to find the ideal point of the ratio of investments in the restructuring and innovation of companies, it is necessary to identify the optimal conditions of the equations:
X1-2X2 = 100000
X1+5X2 = 500000
where X1 – companies’ capitalinvestments; X2 – innovations.
The original problem turns into the maximization problem:
L1 = -x1 + 2×2-5 = max
L2 = x1 + 5×2 + 5 = max
x1-2×2≤247894,
x1≥0,
x2≥0,
Let’s build the feasibleregion. The relevant values x1, x2 are found from the system of linear equations: X1 = 214,285.8 ths. UAH. X2 = 57,142.8 ths. UAH.
A large share of investments in the category “Vehicles and equipment” is due to the growing number of logistics companies in Ukraine each year due to the active phase of the formation of the national market of logistics services and, in this connection, the need for modernization of terminals and other vehicles, including warehouse and trade infrastructure used by relevant companies and enterprises in the process of their economic activity. Figure 2 shows the results of analysis of dynamics of capital investments by types of assets for 2010-2017.
The results of the statistical analysis indicate that based on the fact that most of the investments are made at the expense of own funds of companies and organizations (the most of which are part of the integration corporate structures), it can be concluded that the directions and magnitude of the injection of investment are currently being set by the owners of international corporations with Ukrainian companies being their part. The obtained data suggest again that innovations are financed mainly at the expense of own funds of the companies. In general, the share of companies engaged in innovations for the period of 2013-2017 is rather small – from 16.1% in 2015 (the minimum value) to 17.3-17.7% (2013 and 2017, respectively), which indicates the need to motivate the introduction of innovations in national companies by the state.
Figure 2.Growth rates of capital investments directed to restructuring of companies by types of assets for 2010-2017 (%)
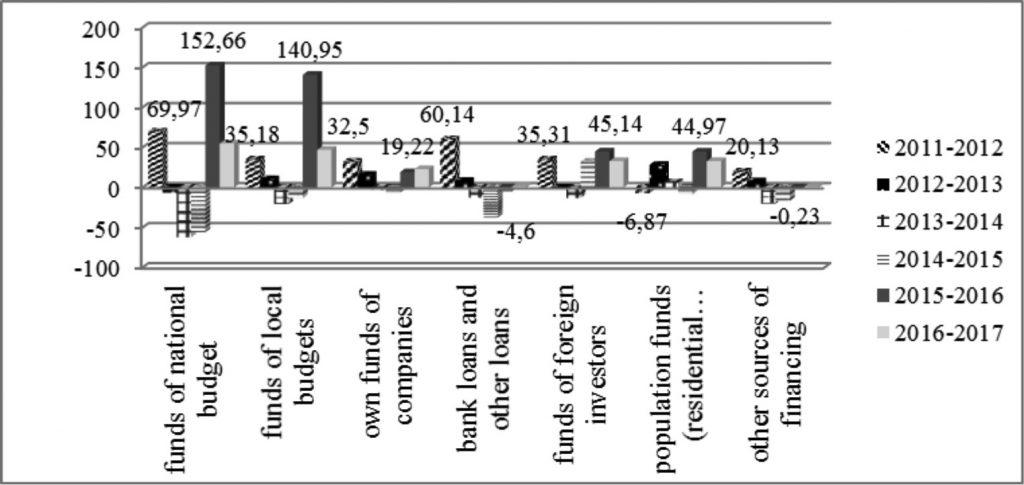
Source: author’s calculations based on (State Statistics Service
of Ukraine, 2018)
According to the results of the survey of the Forbes expert pool: in the ranking of innovative Ukrainian companies with the respondents being the Kyiv-Mohyla Business School, SP Advisors investment company, IBI-Rating ranking agency, Integrites law firm, as well as the representative of the big four – KPMG, according to the level of uniqueness of products and business processes of companies, the most comprehensive complex assessment of the scale of product, marketing and managerial innovations taking into account the level of competitive advantage was received by PrivatBank, Yuzhmash, Nova Poshta (Save the Future: The first rating of innovative companies in Ukraine, 2015).
2. Indices of innovative development of Ukrainian companies. According to the data provided in Forbes analytical materials, indicators of innovation development of the leading Ukrainian companies, which actively implemented and funded innovations according to the ranking list provided by the publication, were analyzed. The sample of these indicators included: costs for innovation activities (I_ in_ a); costs to create an innovative product (I_ in_ pr);
R & D expenses (I R & D ); investment costs for innovation financing (I _ fin _in); costs associated with professional development and training of workers (Itrain) (Innovation development of the enterprise, 2016). This also applies to identification of types and directions of innovative development of national companies, which are also determined according to the needs of integrated companies in virtually all branches of the economy (see Figure 3)
Figure 3.Dynamics of the share of sources of financing of innovation activity in 2012-2017
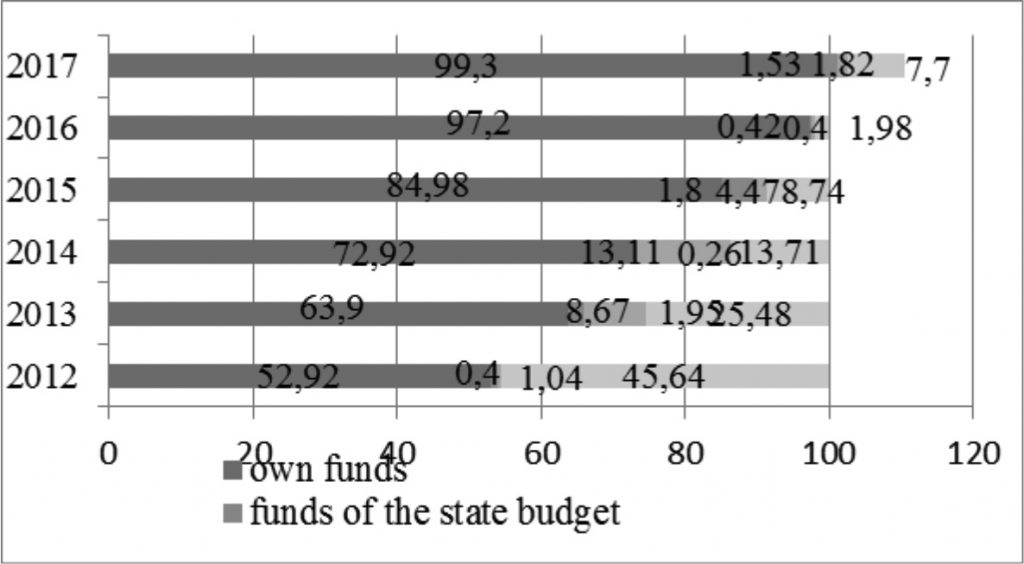
Source: author’s calculations based on (State Statistics Service of Ukraine, 2018)
In order to increase the level of reliability of the results of the analysis of the level of innovative development of the leading Ukrainian companies, weighted average values were used in the process of calculating the index of innovation development taking into account the weighting factors for each indicator. The expert estimation method is used to calculate the indices, the index of innovative development – formula 5.
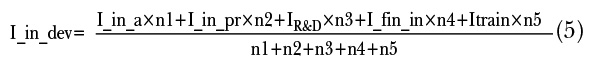
where ni are indices of significance for the following factors of the index of innovation development (calculated using the expert estimation method): n1 (expenditures directed to innovation activity) = 0.25; n2 (expenditures to create an innovative product) = 0.18; n3 (R&D expenditures) = 0.15; n4 (investment expenditures on financing innovative activity) = 0.25; n5 (expenditures related to the employee professional development and training) = 0.17 (Innovation development of the enterprise, 2016).
Discussion. Indices of innovative development of Ukrainian companies and their associations confirm the type of capital investments already introduced in the current research – logistic and agrarian companies. It is seen that the companies that are part of the clusters of companies with the highest rate of innovative development belong to the corresponding corporate entities – groups that have wide opportunities for innovation and able to accumulate a significant investment capital based on the consolidation of all types of corporate resources. This confirms the effectiveness of the new form of the company restructuring – corporatization, which has the highest potential during the period of the development of the national economy, in particular in the innovation and investment context.
Conclusions. The results of the study undertaken have identified that under modern conditions of innovation and investment development of the Ukrainian economy its key element is the efficiency increase of restructuring both on macro- and micro- levels, including the implementation of the state and communal companiesprivatization. In this context based on the critical study of scientific works of Ukrainian and foreign scholars the current study has identified the essence of the term “restructuring.” It has also provided characteristic features of the overall objective and a set of goals within restructuring of economic entities, which undergo different stages of their life cycles (generation, growth, stability, and decline). The mechanism of the company restructuring under the modern conditions of innovation and investment development of the country’s economy has been developed separately. In addition, the current research has identified characteristics of its components by providing main elements: the method of corporate restructuring; strategies of introducing innovations and diversification; such tools of restructuring as takeover and integration; levers of restructuring that are connected with the formation of competitive advantages and the increase of innovation and investment potential of the company.
The study has also revealed that the directions of innovation and investment development of the national economy are oriented on the needs and interests of the owners of large international corporate entities – holdings and groups that direct the largest amount of investment inflows into the activities of Ukrainian companies, in particular, into the innovative development. It is proved that the results of the evaluation of the level of innovative development of companies by the index method enable to predict trends of innovative development of companies. The sectors of the national economy that actively implement innovations and invest in innovative development are finance, logistics, pharmaceuticals, mechanical engineering and the new Ukrainian market –e-commerce. The companies of these industries have the highest indicators of innovation development and, accordingly, the prospects of development in the relevant markets in the years to come.
It is appropriate to focus further studies on the disclosing of problems concerning Ukrainian companies restructuring, especially the integration of national economy to the common European economic space.
References
1. Arafiev, S. O. (2014), Enterprise restructuring: approaches, essence, and components,Manager, 2, pp. 129-134.
2. Commander, Simon (1998), Enterprise Restructuring and Unemployment in Models of Transition,Washington: The World Bank.
3. Prushkivskyi, V.G. (2008), Restructuring of industry in the region: the theory, methodology, practice, Harkiv: Problemiekonomikipromislovihregioniv.
4. Savruk, O.I. (2010), Models and methods of restructuring companies in a market economy,Kyiv: Kyyivskyynatsionalʹnyyekonomichnyy un-t.
5. Santarek, K. (2011),Enterprise restructuring and improvement, AIM 2011 Conference, Skopje, Macedonia, 22-25 September 2011 (retrieved from http://www.europe-aim.eu/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/Santarek-2011-Skopje-K.S.-2011_09_23.pdf).
6. Amsden, A. H. Kochanowicz, J. and Taylor, L. (1994), The market meets its match: Restructuring the economies of Eastern Europe, Harvard University Press.
7. Goldberg, I. and Watkins,A. (2000), Enterprise restructuring, Washington: The World Bank.
8. Carlin, W. Mayer, C. Sinn,H.-W.andGrilli,V. (1992), Restructuring Enterprises in Eastern Europe, Economic Policy, 7, pp. 346-348.
9. Stojčić, N. (2012), Patterns and determinants of enterprise restructuring in Central and East European countries, Ekonomskamisao i praksa, 2, pp. 429-456.
10. Djankov, S. and Murrell, P. (2002), Enterprise restructuring in transition: A quantitative survey, Journal of economic literature, 3, pp. 739-792.
11. Kostiunik, O.V. and Nakonechna, A.A. (2016), Main reasons and peculiarities of implementation of Ukrainian enterprises restructuring, Scientific Journal of Kherson State University: Economics, 17, pp. 143-146.
12. Montes-Negret, F.and Papi, L. (1997), The Polish experience in bank and enterprise restructuring, MOST: Economic Policy in Transitional Economies, 1,pp. 79-104.
13. Charap, J. and Zemplinerova, A. (1993), Restructuring in the Czech economy, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development.
14. State Statistics Service of Ukraine (2018), Net profit (loss) of enterprises based on types of economic activity, 9 April (retrieved from http:// www.ukrstat.gov.ua).
15. State Statistics Service of Ukraine (2018), The number of legal entities based on organizational forms,9 April (retrieved from http:// www.ukrstat.gov.ua).
16. Mordvytska, Yu.S. (2016), The functional approach to improving the system of logistics business processes integrated holdings, Teoretychni i praktychniaspektyekonomiky ta intelektualnojivlasnosti, 1, pp. 61-65.
17. Filimonenkov, O.S. (2002), Finance of companies, Kyiv: Kondor.
18. Tereshchenko, O.O. andVoloshaniuk, N.V. (2009), Financial dominants of enterprises restructuring, FinancyUkrainy, 4, pp. 82-90.
19. Viatrovych, O. (2011), Restructuring as one of the most important ways to provide enterprise activity, Economist, 7 (297), pp. 40-42.
20. Kozytska, G.V. (2008), Restructuring of enterprises under the conditions of market relations: PhD abstract in specialty 08.00.04 “Economics and enterprises management (based on economic activities),” Priazov State Technical University, Mariupol, 20 p.
21. Hoekman, Bernard M.and Pohl, Gerhard (1995), Enterprise Restructuring in Eastern Europe: How Much? How Fast? Where?: Preliminary Evidence from Trade Data,Washington: World Bank Publications.
22. Samonis, Val (1998), Enterprise Restructuring and Foreign Investment in the Transforming East: The Impact of Privatization, London:Routledge.
23. Regulations on the procedure of restructuring of enterprises (2002), OfitsiynyyvisnykUkrayiny, 19, pp. 37.
24. Mordvytska, Yu.S. (2016), Transfer pricing in the management of corporate logistics business processes, Unyversytetskaja nauka-2016, 3, pp. 92-93.
25. Zeman, Z., Kalmar, P., Lentner Cs. (2018): Evolution of Post-Crisis Bank Regulations and Controlling Tools. A Systematic Review from a Historical Aspect. Banks and Bank Systems Vol. 13. No. 2. pp. 130-140.
26. Zeman, Z. Lentner, Cs. (2018) The Changing Role of Going Concern Assumption Supporting Management Decisions After Financial Crisis. Vol. 18. No. 1. pp. 428-441.
27. State Statistics Service of Ukraine (2018), Capital investment based on types of assets,9 April (retrieved from http:// www.ukrstat.gov.ua).
28. State Statistics Service of Ukraine (2018), Sources of innovation activity financing,9 April (retrieved from http:// www.ukrstat.gov.ua).
29. Forbes Ukraine (2016), Save the Future: The first rating of innovative companies in Ukraine,9 April (retrieved from: http://forbes.net.ua/magazine/forbes/1416757-spasti-budushchee-pervyj-rejting-innovacionnyh-kompanij-ukrainy).
30. Innovation development of the enterprise (2016), Methods of evaluation of innovative development of enterprise for five indicators 9 April (retrieved from http://pidruchniki.com/85846/ekonomika/metodika_otsinyuvannya_rivnya_innovatsiynogo_rozvitku_pidpriyemstva_pyatma_pokaznikami).
31. SCM Group (2016), Strategic Management,9 April (retrieved from: http://www.scmholding.com).
32. DTEK Holding (2016), About DTEK Group,9 April (retrieved from: http:// www.dtek.com/uk/home
33. Nova poshta (2016), Business Clients,9 April (retrieved from http:// novaposhta.ua/ru).
Oleksandra Ashcheulova
Ph.D. in Economics, Associate Professor,
National Technical University “Dnipro Polytechnic”, Kyiv, Ukraine
@ WCTC LTD --- ISSN 2398-9491 | Established in 2009 | Economics & Working Capital

