Specific features of ensuring food security in Ukraine
Annotation. The article substantiates that food security is one of the main indicators of socio-economic development of the country. The study suggests that food security is the state of the national economy and the agro-industrial complex in which, regardless of the influence of various internal and external factors, the satisfaction of the population’s needs for food consumption with rational consumption norms is guaranteed, and the food independence of the country is ensured. On the basis of the Global Food Security Index, negative trends in the level of food security in Ukraine in 2014-2016 are identified. The most important factors influencing the level of food security in Ukraine are grouped and characterized by author. The main tasks for the formation of a satisfactory level of food security are identified, among which are as follows: the technological modernization of agriculture, food industry and agribusiness production services; the formation of the personnel potential, able to develop and implement innovations; the restoration of agricultural production in abandoned agricultural lands; the creation of modern social infrastructure of rural areas. According to the proposed measures, a conceptual model of the mechanism for ensuring food security in Ukraine was developed.
Key words: agro-food sphere, security, threats, protection, the mechanism for ensuring food security, food products, the level of food security.
Setting of a problem. At the present stage of the development of society, the problem of ensuring food security is becoming increasingly important. Moreover, it is considered one of the key problems of a global nature. Therefore, its solution is an important condition for creating an atmosphere of stability and prosperity both in the world as a whole and in each country in particular. In just the last decade alone, the following changes have occurred in the sphere of food consumption: about 140 million people who are below the poverty line do not have the opportunity to be provided with food products in a volume that corresponds to physiological consumption norms [21].
In Ukraine, in 2016, food consumption, as compared to similar indicators of the late 1980s, declined as follows. Consumption of fish and fish products declined by 3,3 times, consumption of milk and dairy products declined by more than 1,2 times, consumption of meat and meat products, eggs, sugar, fruits and berries declined almost 80%, and finally, consumption of vegetable oil and vegetables declined by 27%. At the same time, consumption of bread, bread products and potatoes has increased. According to various estimates, the daily energy content of the diet of a resident of Ukraine has significantly decreased compared to 1990 from 3420 kcal to 2460-2100 kcal. The same situation is observed in the post-Soviet countries [21, 22].
Radical liberalization of the Ukrainian economy in 1991-1992 and the subsequent dismantling of managerial, financial, credit, price, tax and other systems have led to an aggravation of the old and the emergence of new problems. At the same time, radical reforms accompanied a decline in agro-food production and a reduction in real incomes of the population. As a result, there was a significant disparity in prices for agricultural products and industrial inputs, the problem of food security in Ukraine as a whole, and its regions, in particular, worsened. The described problem is international, in former socialist countries {25, 26, 27}, what’s more in China too {28}, manly on financial path, inherently by bank and credit policy.
The need to develop a food security strategy is the absence of a food security system that has been purposefully created and developed by the subjects of state and local government, economic entities of all spheres and subsystems that ensure food security at the national, regional and local scales.
Awareness of the real state and the need to ensure food security leads to the conclusion that the chaotic and uncontrolled state of subsystems for ensuring food security, which are functionally, organizationally, resourcefully and technologically related, should be replaced by a corresponding system of food security of the country and regions that would include regional and local authorities together with the commodity producers and scientific sphere, financial business and agrarian business entities.
Analysis of recent researches and publications. Despite the fact that the problem of ensuring an adequate level of food security, including the various theoretical aspects of its definition and measurement in the context of globalization challenges, has been sufficiently specified in the scientific works of leading economists, specialists in management theory and practitioners of the agro-food sector, we have to state that some aspects of this problem still remain controversial. This concerns first of all the definition of the essence of the phenomenon of food security, the legislative regulation of food security issues and the diagnosis of the level of food security.
The etymology of the term “food security” makes it possible to determine its introduction into practice in 1974 at the World Food Conference, organized by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), held in Rome after the steep rise in world grain prices. However, the essence of this category was determined in 1996 in the Rome Declaration on World Food Security, where it is noted that food security, at the individual, household, national, regional and global levels is achieved when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life” [11].
The study of the problem of food security has its origins in the early 20th century. In particular, Kondratiev N., Chayanov A. and Bukharin N. [15] in the 60s of the 20th century pointed out the relationship between consumption and production of agro-food products [16]. The establishment of optimal proportions between production and consumption was further investigated in the scientific works of Bilous O.H. [19], Vlasov V.I. [19], Yeszhanova Zh.Zh. [15] and
Zerkalov D.V. [15]. A significant contribution to solving the problem of ensuring food security was made by such famous Ukrainian and foreign scientists as: Pruntseva H.О. [18], Sabluk P.T. [19], Sidnieva Zh.K. [20], Tarakhov P.V. [21], Tryn’ko R.І. [22], Uskova T.V. [23], Tsarenko O.М. [24], Shcherban’ V.M. [24] and many others.
Currently, the area of ensuring food security is still one of the main directions of the state’s economic policy, as well as the main condition for social stability and the basis for improving the quality of life of the population.
Goal setting. The purpose of this study is to analyze the concept of food security for the domestic economy, to determine its level and to develop a mechanism for ensuring food security of the country.
Presentation of basic material of the research. In the second half of the 1990s, the term “food security” became widely used both in official documents and in scientific literature. The analysis of sources on the problem under study allows us to state that today there is no clear, scientifically based and normatively fixed idea of this category in Ukraine.
According to the concept of food security proposed by Maxwell and Frankenberd [15], food security is defined as an opportunity to purchase food products, necessary to maintain a healthy and active life, at any time. Additionally, the arbitrary use of the term “food security”, as was the case in the draft of a “National Program for the Development of Agro-Industrial Production and the Social Revival of the Village of Ukraine for 1999-2010 threatens that all other resources will be directed to “raising agriculture”, the supply of which will be provided by demand from the broad sections of the population [5]. The proposed strategy of agrarian policy in Ukraine, the essence of which is reduced to the food security of the country, is aimed primarily at achieving food self-sufficiency in the minimum necessary amount of food and reviving the viability of the country’s agricultural sector and the core principles of its functioning.
An important element of the state regulation of food security and the national economy as a whole is the formation of the state food reserve. The regulatory legal basis framework for the formation of the food reserve in Ukraine includes the Law of Ukraine “About the State Budged of Ukraine” [10], the Law of Ukraine “About State Support of Agriculture of Ukraine” [2], the Law of Ukraine “About the State Order for Satisfaction of Priority State Needs” [1], the Law of Ukraine “On the Fundamentals of the State Agrarian Policy for the Period until 2015” [3], the Law of Ukraine “On the State Material Reserve” [9], the Decree of the President of Ukraine “On the Approval of the Statute on the State Agency of the Reserve of Ukraine” [4], the Order of the Minister of Agrarian Policy of Ukraine “On the Implementation of Financial Interventions by the Agrarian Fund” [7].
The Decree of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine “On the adoption of the Draft Law of Ukraine on Food Security of Ukraine” emphasizes that the critical situation with food supply of the population is one of the threats to national interests and national security as a whole [8].
The general essence of food security of Ukraine is adequately reflected in the existing normative and legislative acts, which are based on international approaches taking into account national economic opportunities. According to the Decree of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine “On the adoption of the Draft Law of Ukraine on Food Security of Ukraine as a basis”, food security should be interpreted as the protection of the vital interests of man and citizen, society and the state, which not only guarantees physical and economic availability to the population of the quality vital food products, but also supports the stability of food provision and provides food independence of the country.
This important concept is very well complemented by scholars of agricultural economics, who believe that “the key characteristics of food security are related to the accessibility, stability and sustainability of access to food products, which largely depend not only on the growth of agricultural production, but also on trade policy, the development of trade ties in the agrarian products markets, that are able to strengthen these characteristics to a certain positive level” [8].
Tryn’ko R.І. argues that “food security is an important and special component of the national security; therefore, it should be viewed not only as an internal component of the state’s independence, but also as an important external factor, since the provision of food for the population at the level of rational consumption norms testifies to the economic strength of the state” [22]. This means that food security in the hierarchy of various types of security should take a special place, since normal and full-fledged food products do not have alternative substitutes.
The idea of treating food security taking into account some economic and environmental positions deserves appropriate attention.
According to the researchers, “the formation of a national food security strategy is related to the economic responsibility for the quality of food and environment of all links of agro-industrial production” [24]. It is characteristic that the formation of food security, taking into account the ecological component of domestic agricultural production, is to a certain extent complicated by the lack of an effective quality control system, in particular the presence of especially hazardous substances such as dioxin, causative agents of mad cow disease, heavy metals, etc. In such a situation, an increase in the level of consumption of agro based and processed food products can definitely create threats to life, or lead to a decrease in the level of health of the population [19].
So, based on the analysis of the existing theoretical provisions on the definition of “food security”, we can conclude that the main distinguishing features of ensuring food security of the country include the following ones:
- the need for physical and economic access of the population of the country to basic food products in the amount necessary for an active healthy lifestyle;
- provision of a set of legal, socio-political, economic, scientific, technical, organizational, information and other measures aimed at ensuring the population’s access to food items;
- the ability of the national food system to minimize the impact of seasonal, weather and other fluctuations in food supplies of the population of all regions of the country.
Consequently, it is proposed to understand food security as a state of the national economy and the agro-industrial complex, in which, regardless of the influence of various internal and external factors, the satisfaction of the population’s needs for food consumption with rational consumption norms is guaranteed, and the food independence of the country is ensured. In modern conditions, the issue of the level of food security is becoming more urgent.In the context of Ukraine’s integration into the world economic community and further transformation of the national economy, the problem of ensuring food security is of paramount importance.
Globalization makes new demands on providing the population with quality food products. Moreover, the national security of the country is largely determined by the level of food security. This problem is quite complex and multifaceted; it directly concerns the interests of each person and the interests of the state as a whole. To this end, “The Economist Intelligence Unit”, which is the research and analysis division of The Economist Group, has published the results of the Global Food Security Index ranks. In 2014-2016, the study of the global food security rankings covered 109 countries, which were evaluated in three main categories:
- level of food availability and consumption;
- availability and sufficiency of food products;
- level of quality and security of food products [13].
Each of these criteria includes 28 different indicators, the values of which are measured over a two-year period. The calculation used data from international organizations and national institutions. The high position of any country in the rating means that its food security is at a high level.
The index measures the achievements of each country on a scale from 0 (the lowest degree of stability) to 100 (the highest degree of stability) on the basis of the data obtained in the three above-mentioned basic categories (See Figure 1).
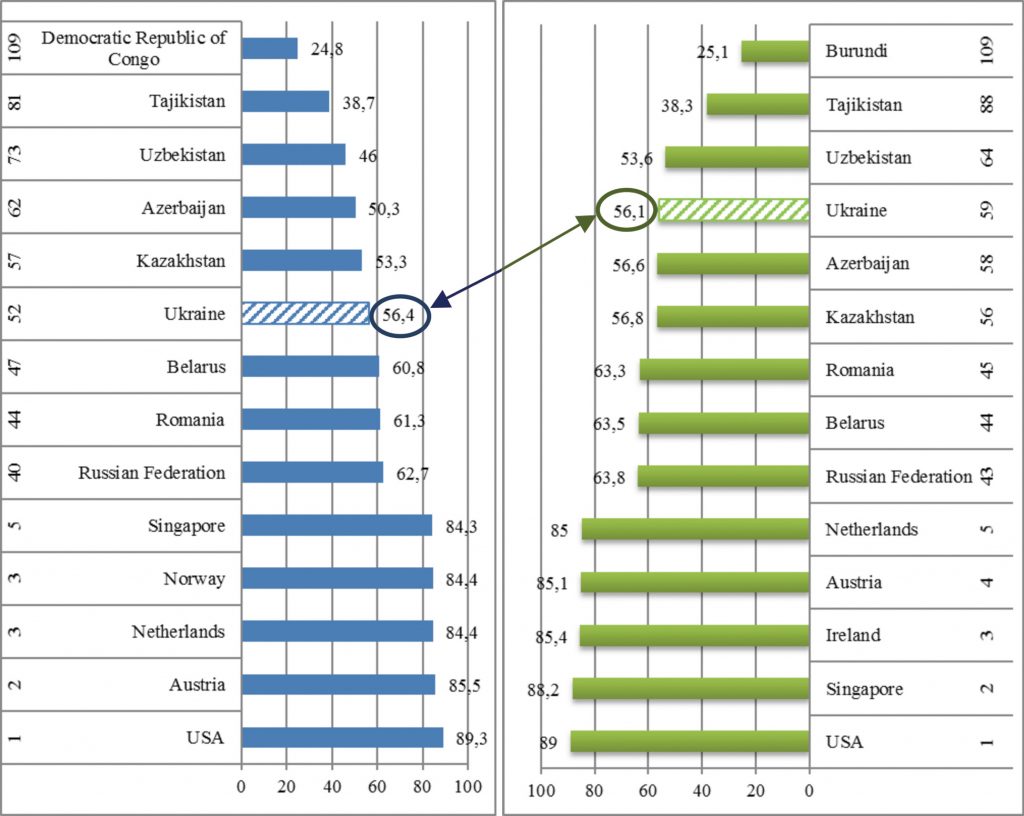
Fig. 1. The Global Food Security Index in 2014 and 2016 [developed by author
on the basis of the sources: 12, 13, 17]
The United States of America became the world leader in the level of food security, and took the first position in the previous rating of 2014. The main advantages of the United States, according to the compilers of the rating, are related to the economic stability of this country, as well as the high level of incomes of its population combined with the relatively low share of household expenditure on food, the developed agricultural and logistical infrastructure, the high diversification of nutrition and the comprehensive access of people to safe and nutritious products. The top ten leaders in terms of food security also included: Singapore, Ireland, Austria, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Canada, Australia, France and Norway [13].
Ukraine ranks 59 out of 109 in the ranking – between Azerbaijan and Ecuador. Over the past two years, this indicator has deteriorated by 8 points. According to experts’ opinion, about 9% of the population of Ukraine does not receive enough nutritious food, necessary for active and healthy lifestyle.
Food security for Ukraine is one of the central problems in the national security system, since without reliable food supply it is not even possible to avoid dependence on other countries.
The following factors influence the food security situation in Ukraine:
- level of development and sustainability of agricultural production;
- income and quality of nutrition of population;
- availability of food products of domestic production;
- the import scales;
- openness of food markets, mechanism of counteraction of import intervention;
- volumes of food stocks;
- production potential of agriculture;
- quality of agricultural products and food products;
- conformity of food security requirements to the legal legislation, as well as to the existing system of normative acts and the priority directions of the agrarian policy of the state;
- threats to food security.
That is, to approach the level of the developed countries, it is necessary to solve simultaneously several interrelated and capital-intensive tasks, which are the next ones:
- the technological modernization of agriculture, food industry and agribusiness production services;
- he formation of the personnel potential, able to develop and implement innovations;
- the restoration of agricultural production in abandoned agricultural lands, including an increase in crops;
- the creation of modern social infrastructure of rural areas (housing, roads, etc.), transition to rural development policy. To this end, it is necessary to constantly monitor price parity between the agricultural sector and other sectors of the economy, to use indicative prices for the timely adoption of measures to ensure the profitability of the production of meat, milk, grain, sugar and other vital food products [15].
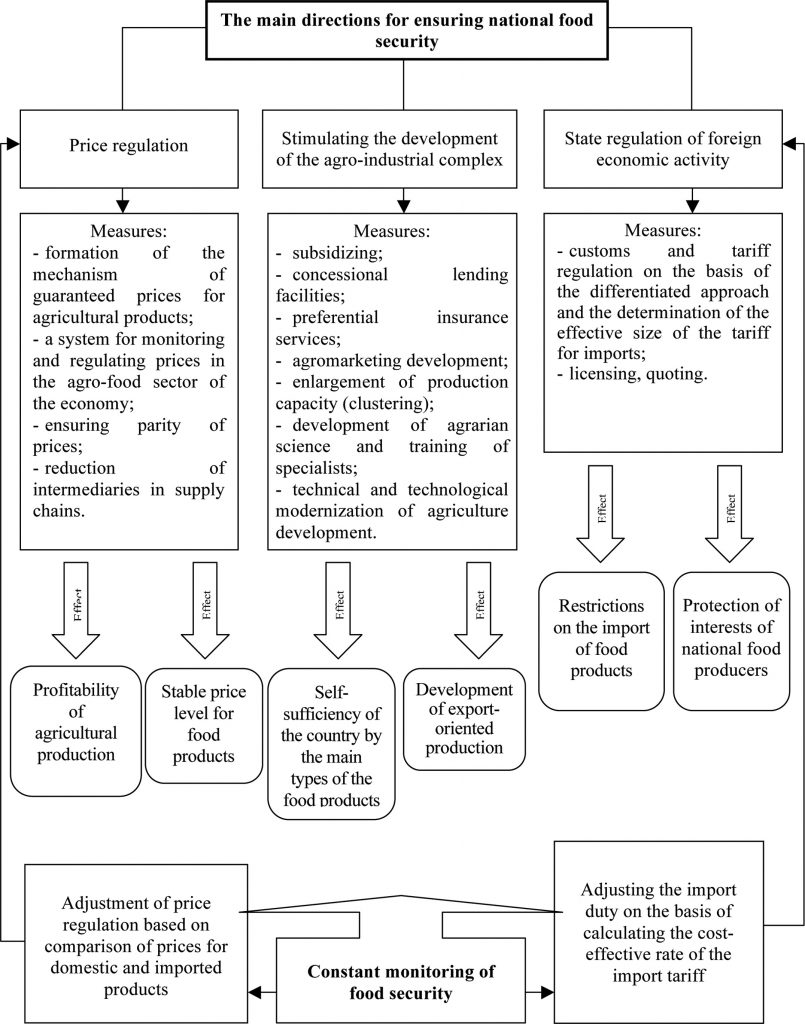
According to the proposed measures, a conceptual model of the mechanism for ensuring food security in Ukraine was developed (See Figure 2).
Fig. 2. The conceptual model of the mechanism
for ensuring food security in Ukraine [developed by author on the basis of the source: 15]
Proceeding from the above-stated considerations, food security of the country largely depends on the agro-food sector, which, with preservation and improvement of the habitat environment, regardless of external and internal conditions, allows the population of the country to continuously receive environmentally friendly and healthy food at affordable prices, in volumes not lower than the level of rational consumption norms.
The most important conditions for achieving food security in Ukraine are the following ones:
- potential physical accessibility of food for each person;
- economic opportunity to purchase food for all social groups, including the poor, which is achieved by raising the standard of living or by taking the necessary social protection measures;
- consumption of high-quality food products in quantities sufficient for a balanced diet;
- creation of stable economic conditions for the development of the national food market;
- conducting of an effective agro-food policy;
- ensuring equal opportunities for all business entities;
- conducting of a reasonable national policy in the field of employment;
- implementation of social policy, aimed at eradicating poverty and social inequality in access to adequate food, as well as its use;
- achieving sustainable, intensive and diverse food production, as well as increasing productivity and efficiency in agriculture;
- implementation of integrated strategies for the development of the agro-industrial sector with a view to increasing local food production opportunities;
- assistance in the introduction of advanced technologies in the production, processing, storage and sale of raw materials and foodstuffs;
- taking advantage of the international division of labour;
- active foreign economic activity and optimization of export-import activities;
- investment in the agrarian sector.
Conclusions. The country’s food security is ensured by a combination of economic and social conditions related both to the development of the domestic agriculture and the agro-food complex, and to the general state of the national and world economy. Consequently, the use of legislatively approved methods of price regulation in the agro-food market, as well as the implementation of the proposed measures for the sustainable development of the agro-food sector of the economy and the reform of the customs policy on the regulation of import foreign trade operations will enable Ukraine not only to strengthen its economic sovereignty, but also to pursue an independent economic policy in the context of globalization, and to determine the possibility of achieving full food security of the country.
Iryna Markina,
D.Sc. (Economics), Professor,
Head of the Department of Management,
Poltava State Agrarian Academy
References
1. About the State Order for Satisfaction of Priority State Needs: The Law of Ukraine of December 22, 1995 No. 493/95-ВР (with amendments and additions) [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/493 /95-вр
2. About State Support of Agriculture of Ukraine: The Law of Ukraine of June 24, 2004 No.1877-IV (with amendments and additions) [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/1877-15
3. On the Fundamentals of the State Agrarian Policy for the Period until 2015: The Law of Ukraine of October 18, 2005 No. 2982-IV (with amendments and additions) [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/2982-15
4. On the Approval of the Statute on the State Agency of the Reserve of Ukraine: the Decree of the President of Ukraine of April 13, 2011 No. 463/2011 [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/517-2014-п
5. Law of Ukraine: About the National Development Program agricultural production and social Village revival for 1999 – 2010, from 23.03.99 [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://w1.c1.rada.gov.ua/pls/zweb2/webproc34?id =&pf3511=5704&pf35401=5810
6. On the Approval of the Volume of the Formation of the State Intervention Fund for the 2017/18 marketing period: Resolution of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine of March 05, 2012 No. 172 [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://minagro.gov.ua/node/22227
7. On the Implementation of Financial Interventions by the Agrarian Fund: Order of the Minister of Agrarian Policy of Ukraine of October 07, 2005 No.543 (with amendments and additions) [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://consultant.parus.ua/?doc=02XLG0FCC1
8. Decree of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine “On the adoption of the Draft Law of Ukraine on Food Security of Ukraine as a basis” [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://zakon3.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/3498-17
9. On the State Material Reserve: The Law of Ukraine of January 24, 1997 No. 51/97-ВР [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://zakon3.rada.gov.ua/ laws/show/51/97-вр
10. About the State Budget of Ukraine for 2017: The Law of Ukraine of December 21, 2016 No. 1801-VIII [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://zakon3.rada.gov.ua /laws/show/1801-19
11. The Rome Declaration on World Food Security (Rome, November 13, 1996) [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://www.g20civil.com/ru/documents/205/577/
12. Humanitarian technologies: analytical portal. Economist Intelligence Unit: The Global Food Security Index in 2014. – [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://gtmarket.ru/news/2014/05/29/6788
13. Humanitarian technologies: analytical portal. Economist Intelligence Unit: The Global Food Security Index in 2016 [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://gtmarket.ru/news/2016/01/29/7291.
14. Markina I. Administrative-legal mechanism of economic security system of the country / I. Markina / Scientific Economic Journal «Actual Problems of Economics», 2016. – №9. – С. 69-77.
15. Yeszhanova Zh.Zh. Mechanism for ensuring food security in the Republic of Kazakhstan / Author’s abstract on degree of Candidate of Economic Sciences.… 08.00.05 – Economics and Management of National Economy (on branches and spheres of activity) // Zh.Zh. Yeszhanova. – Almaty, 2009. – 30 p.
16. Zerkalov D.V. Food security [monograph] / D.V. Zerkalov. – Kyiv: Osnovy Publishing, 2009. – 405 p.
17. Food security [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: https://lektsii.org/7-46924.html
18. Pruntseva H.О. Economic essence of the term “food security” of the country / H.O. Pruntseva // Innovative Economy: Scientific and Production Journal. – 2016. – Vol. 1-2. – P. 34-37.
19. Sabluk P.T. Food security of Ukraine / P.T. Sabluk, O.H. Bilous,
V.I. Vlasov // The Economy of Agro-Industrial Complex: International Scientific and Production Journal. – 2009. – Vol. 10. – P. 3-7.
20. Sidnieva Zh.K. Food security of Ukraine in conditions of market transformations / Zh.K. Sidnieva // Institutional framework of the economy functioning in conditions of transformation: collection of scientific articles. – Nuremberg, Germany. – Vol. 2, 2014. – Р. 235-238.
21. Basic components of food security [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: http://www.nirsi.ru/business/prodovolstvennaya-bezopasnost/
22. Tryn’ko R.І. Food security: analytical diagnostics [monograph] / R.I. Tryn’ko. – Lviv, 2010. – 168 p.
23. Uskova T.V. Food security of the region [Electronic resource]. – Retrieved from: https://econ.wikireading.ru/4497
24. Tsarenko O.М. Ecologization of production as the basis of food security in Ukraine / О.М. Tsarenko, P.V. Tarakhov, V.M. Shcherban’ // The Economy of Agro-Industrial Complex: International Scientific and Production Journal. – 2001. – Vol. 5. – P. 15-20.
25. Széles, Zs., Zéman, Z., Zsarnóczai J. S. The developing trends of Hungarian agricultural loans in term of 1995 and 2012, Agricultural Economics-Zemedelska Ekonomika, 2014, Vol. 60 no. 7, pp. 323-331.
26. Lentner, Cs. Szigeti, C. Borzan, A. Possibilities and Problems Financing the Hungarian Agriculture, Revista Tinerilor Economisti, 2007, Vol. 5. Special Issue, pp. 111-116.
27. Lentner, Cs. Szigeti C, Borzan A. Agricultural credit policy in Hungary, Miznarodnij Zbirnik Naukovih Prac, 2008, Vol. 10. no. 1. pp. 186-191.
28. Maohua L, Zéman Z. Study on the srid evaluation framework of agricultural enterprises in China, Visegrad Journal of Bioeconomy and Susbstainable development, 2016, Vol. 5. no. 1. pp. 36-40.
@ WCTC LTD --- ISSN 2398-9491 | Established in 2009 | Economics & Working Capital

